The Nutanix Cloud Bible
The purpose of The Nutanix Cloud Bible is to provide in-depth technical information about the Nutanix platform architecture and how it can enable smooth operations across cloud, edge, and core environments.
» Download this section as PDF (opens in a new tab/window)
The Nutanix Objects feature provides highly scalable and durable object services via an S3 compliant API (More Information on S3: LINK). Given Nutanix Objects is deployed on top of the Nutanix platform, it can take advantage of AOS features like compression, erasure coding, replication and more. Objects was introduced in AOS 5.11.
The solution is applicable to the configurations below (list may be incomplete, refer to documentation for a fully supported list):
Core Use Case(s):
Management interfaces(s):
Hypervisor(s):
Upgrades:
Key Features:
Supported Protocols:
Nutanix Objects leverages the Nutanix Microservices Platform (MSP) and is one of the first core services to do so.
Nutanix MSP provides a common framework and services to deploy the Objects component's associated containers and platform services like Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Load Balancing (LB).
The following key terms are used throughout this section and defined in the following:
The figure shows the high-level mapping of the conceptual structure:
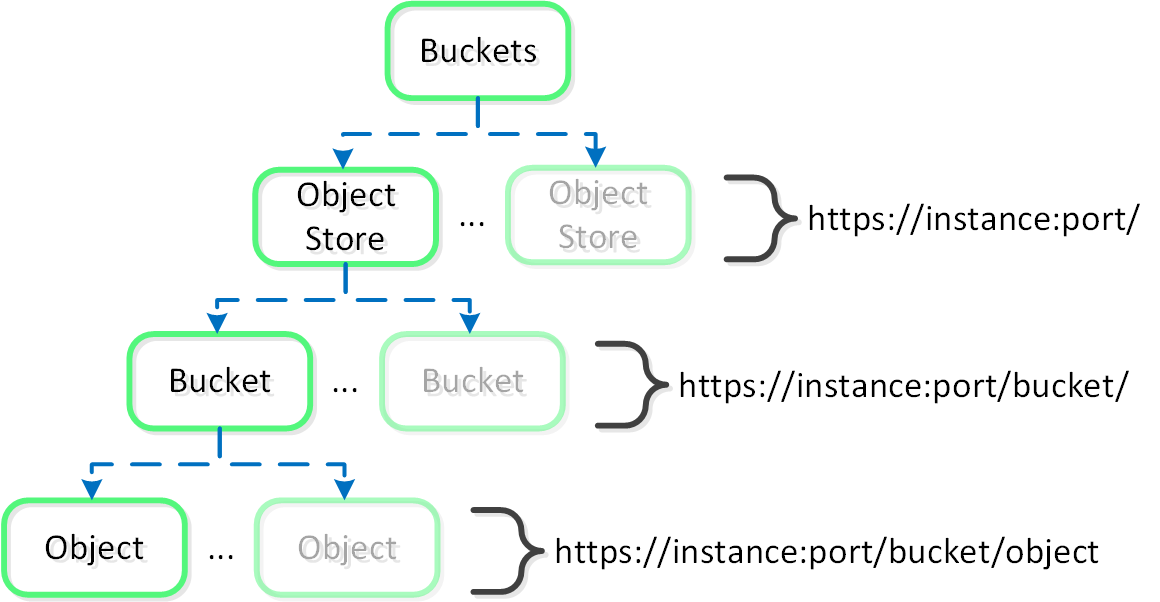 Objects - Hierarchy
Objects - Hierarchy
This feature is composed of a few high-level constructs:
The figure shows a detailed view of the Objects service architecture:
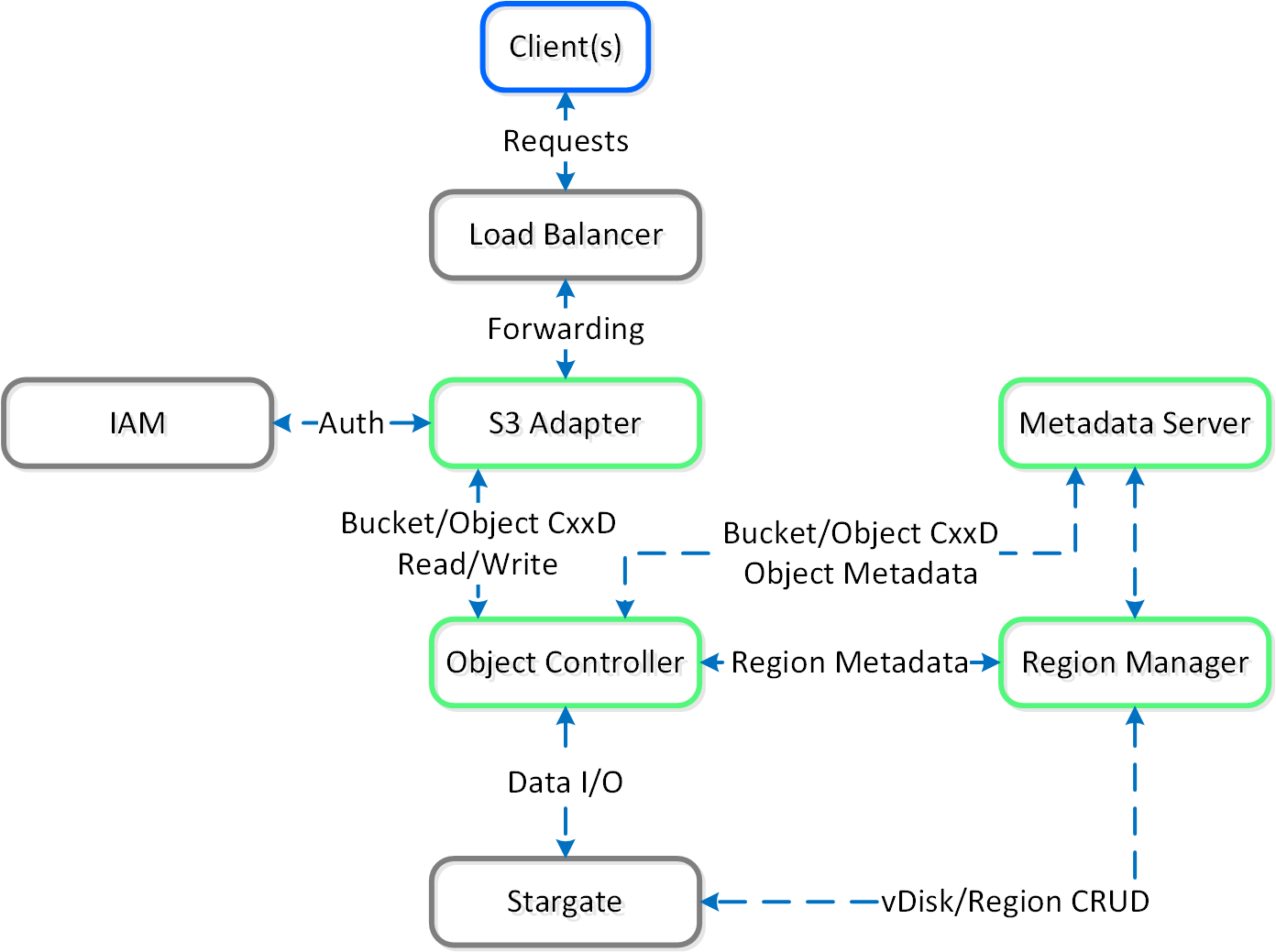 Objects - Architecture
Objects - Architecture
The Objects specific components are highlighted in Nutanix Green. With objects there’s no concept of an “overwrite” hence the CxxD vs. CRUD (Create/Replace/Update/Delete). The commonly employed method for an object “overwrite” is to create a new revision or create a new object and point to the new object.
Nutanix Objects is built using a combination of organic innovation while also leveraging open source components. We believe this makes our products more robust and performant giving our customers the best solution for their business.
More Information on our Open Source License Disclosures: LINK
An object is stored in logical constructs called regions. A region is a fixed segment of space on a vDisk.
The figure shows an example of the relationship between a vDisk and region:
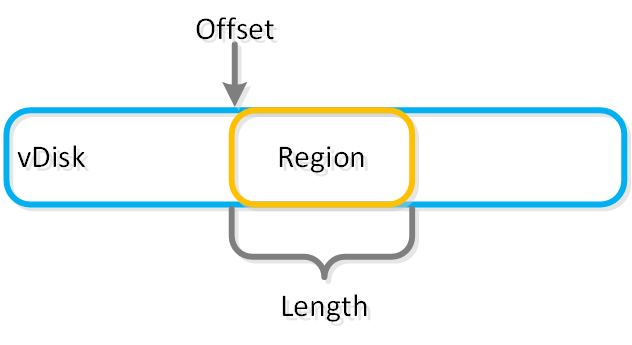 Objects - vDisk Region
Objects - vDisk Region
Smaller objects may fit in a chunk of a single region (region id, offset, length), whereas larger objects may get striped across regions. When a large object is striped across multiple regions these regions can be hosted on multiple vDisks allowing multiple Stargates to be leveraged concurrently.
The figure shows an example of the relationship between a object, chunk and region:
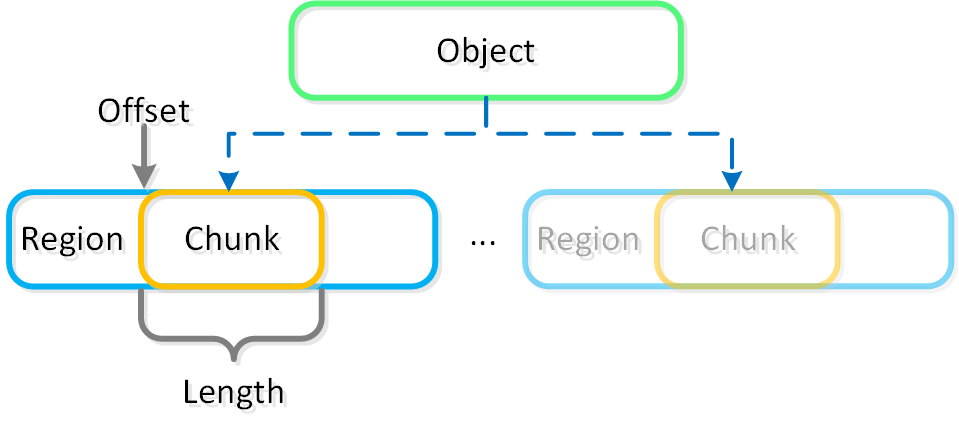 Objects - Object Chunk
Objects - Object Chunk
The object services feature follows the same methodology for distribution as the Nutanix platform to ensure availability and scale. A minimum of 3 object VMs will be deployed as part of the Objects deployment.
©2025 Nutanix, Inc. All rights reserved. Nutanix, the Nutanix logo and all Nutanix product and service names mentioned are registered trademarks or trademarks of Nutanix, Inc. in the United States and other countries. All other brand names mentioned are for identification purposes only and may be the trademarks of their respective holder(s).