The Nutanix Cloud Bible
The purpose of The Nutanix Cloud Bible is to provide in-depth technical information about the Nutanix platform architecture and how it can enable smooth operations across cloud, edge, and core environments.
» Download this section as PDF (opens in a new tab/window)
When a Nutanix Hyper-V cluster is created we automatically join the Hyper-V hosts to the specified Windows Active Directory domain. These hosts are then put into a failover cluster for VM HA. When this is complete there will be AD objects for each individual Hyper-V host and the failover cluster.
In Hyper-V deployments, the Controller VM (CVM) runs as a VM and disks are presented using disk passthrough.
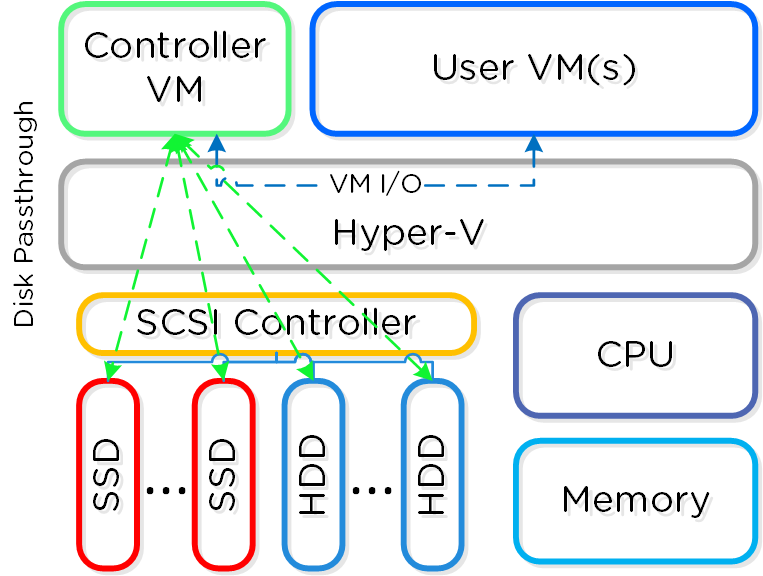 Hyper-V Node Architecture
Hyper-V Node Architecture
The following configuration maximums and scalability limits are applicable:
NOTE: As of Hyper-V 2012 R2 and AOS 6.6. Refer to Configuration Maximums for other versions.
Each Hyper-V host has a internal only virtual switch which is used for intra-host communication between the Nutanix CVM and host. For external communication and VMs a external virtual switch (default) or logical switch is leveraged.
The internal switch (InternalSwitch) is for local communication between the Nutanix CVM and Hyper-V host. The host has a virtual ethernet interface (vEth) on this internal switch (192.168.5.1) and the CVM has a vEth on this internal switch (192.168.5.2). This is the primary storage communication path.
The external vSwitch can be a standard virtual switch or a logical switch. This will host the external interfaces for the Hyper-V host and CVM as well as the logical and VM networks leveraged by VMs on the host. The external vEth interface is leveraged for host management, live migration, etc. The external CVM interface is used for communication to other Nutanix CVMs. As many logical and VM networks can be created as required assuming the VLANs are enabled on the trunk.
The following figure shows a conceptual diagram of the virtual switch architecture:
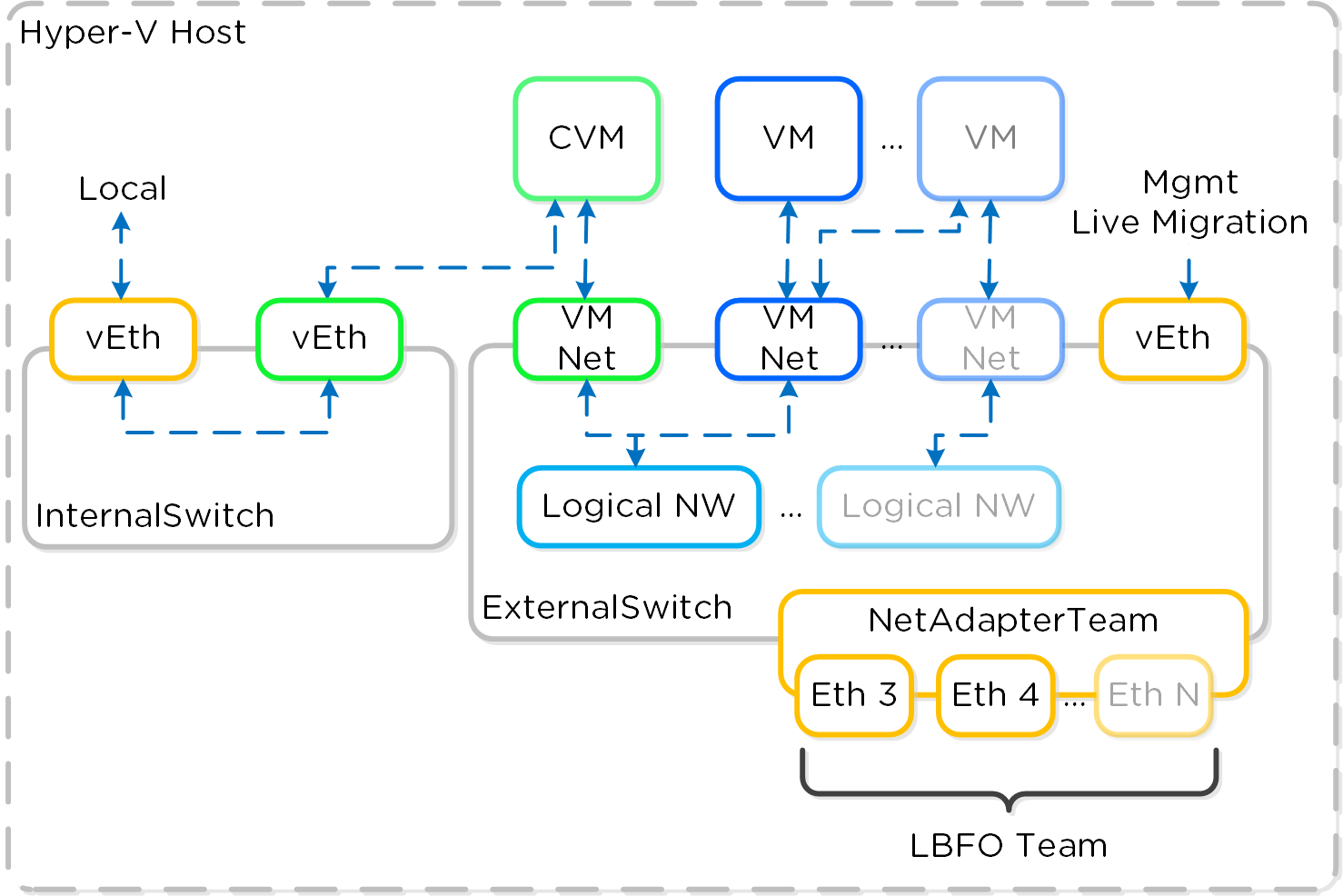 Hyper-V Virtual Switch Network Overview
Hyper-V Virtual Switch Network Overview
It is recommended to have dual ToR switches and uplinks across both switches for switch HA. By default the system will have the LBFO team in switch independent mode which doesn't require any special configuration.
©2025 Nutanix, Inc. All rights reserved. Nutanix, the Nutanix logo and all Nutanix product and service names mentioned are registered trademarks or trademarks of Nutanix, Inc. in the United States and other countries. All other brand names mentioned are for identification purposes only and may be the trademarks of their respective holder(s).