The Nutanix Cloud Bible
The purpose of The Nutanix Cloud Bible is to provide in-depth technical information about the Nutanix platform architecture and how it can enable smooth operations across cloud, edge, and core environments.
» Download this section as PDF (opens in a new tab/window)
Microservices Infrastructure (MSP) provides a common framework for delivering microservices associated with Prism Central-based components such as Flow Virtual Networking, Objects, and the Security Dashboard. MSP also provides services such as Identity and Access Management and internal service load balancing.
Before MSP, Prism Central was a monolithic application. With MSP enabled, certain services are migrated and spun up in a Kubernetes (K8s) cluster as pods. Over time, most of the Prism Central services will be migrated and converted to microservices leveraging the common platform. This will enable services to be upgraded independently through LCM, so particular services can be upgraded without having to upgrade the entire PC instance, resulting in faster upgrades and quick patch updates.
As of PC.2022.9, the Microservices Infrastructure is enabled by default. When you upgrade to the latest version of Prism Central, MSP will be automatically enabled. Refer to the Prism Central MSP documentation for the full list of prerequisites and considerations.
When MSP is enabled, a Kubernetes cluster is created on Prism Central. This Kubernetes cluster is one node with a standalone Prism Central and three nodes with a scale-out Prism Central.
MSP uses the following subnets.
| Subnet | Purpose |
| 10.100.0.0/16 | Reserved for K8s pod network |
| 10.200.32.0/24 | K8s Services (Flow Virtual Networking, IAM, etc) |
| 10.200.0.0/16 | Reserved for K8s Services network |
| 10.100.0.0/24 | K8s pod - PC1 |
| 10.100.1.0/24 | K8s pod - PC2 |
| 10.100.2.0/24 | K8s pod - PC3 |
If you already use these subnets for DNS or Active Directory and require different IP ranges, contact Nutanix Support.
On the firewall, bidirectional traffic should be allowed between Prism Central and:
On TCP ports:
Additionally, Prism Central should be able to ping all the Prism Element CVM IPs and Prism Element Virtual IPs.
During deployment, Prism Central must access several cloud services over port 443. For the most up-to-date list and diagrams, refer to the Ports & Protocols page on the Support Portal. There is also a dark site method of deployment for networks without Internet access, which is covered in the Prism Central MSP documentation.
When deploying Prism Central or enabling MSP, there are two options for the internal network configuration.
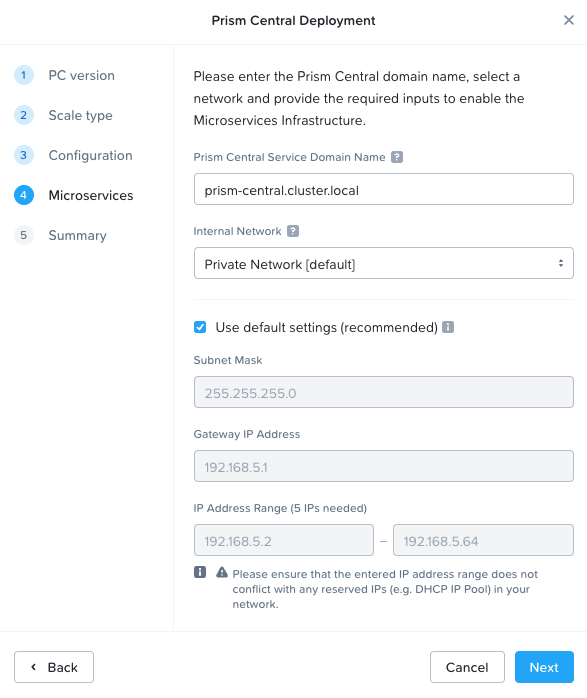 Microservices Setup During Prism Central Deployment
Microservices Setup During Prism Central Deployment
The diagrams below assume the default private VXLAN network.
An example architecture diagram for the Kubernetes node on a single-PC deployment looks like the following. Note that the example does not show every service running in the Kubernetes cluster.
In this example, 10.10.250.50 is the IP address assigned to the PC VM and 10.100.0.0/24 is used as the network for the Kubernetes pod.
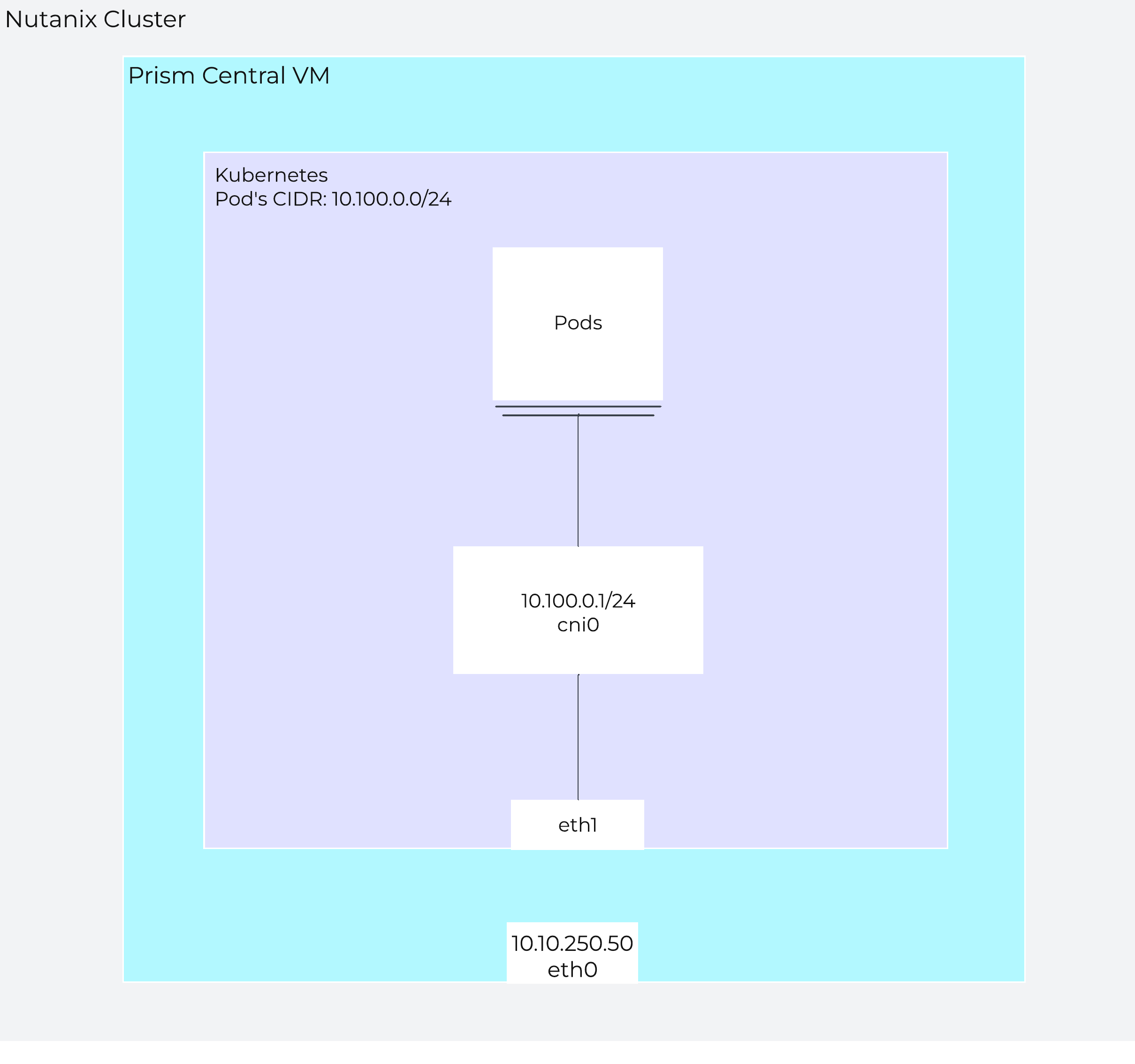 Single Node PC
Single Node PC
For scale-out PC, two additional Kubernetes nodes are provisioned and they use the 10.100.1.0/24 and 10.100.2.0/24 networks for their pods, respectively.
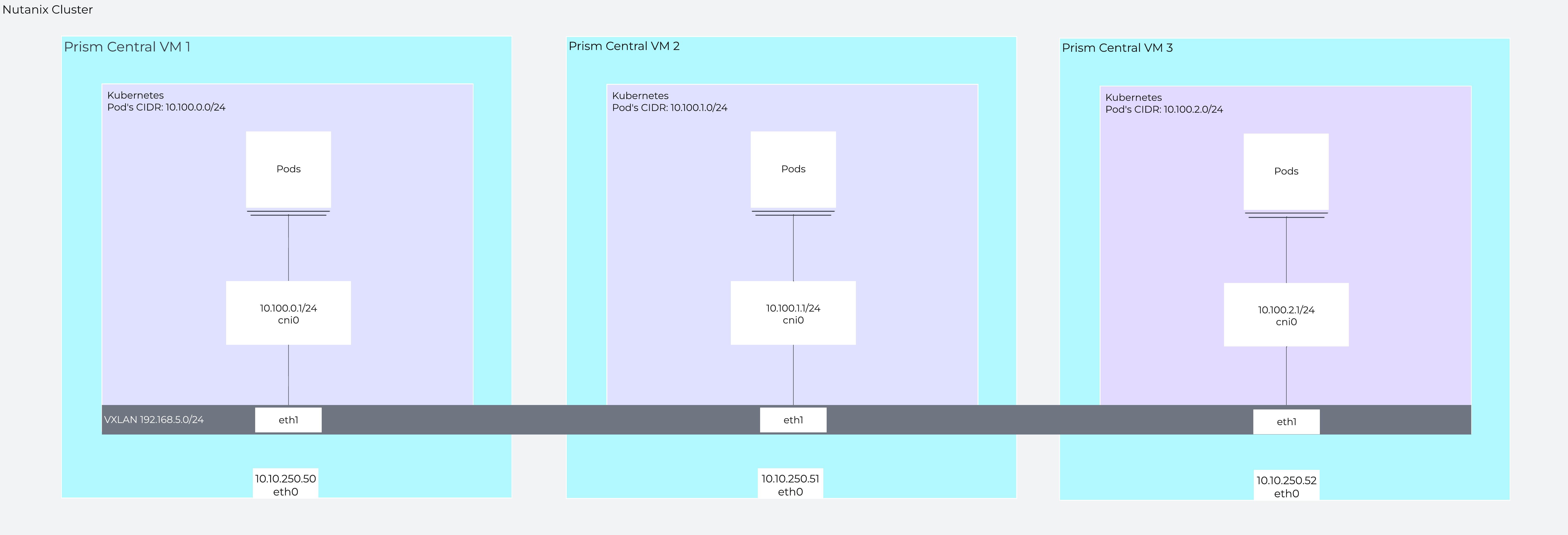 Scale-out PC
Scale-out PC
In a scale-out PC setup with VXLAN, pod-to-pod traffic across nodes uses direct routing and is encapsulated using the Prism Central VM IP.
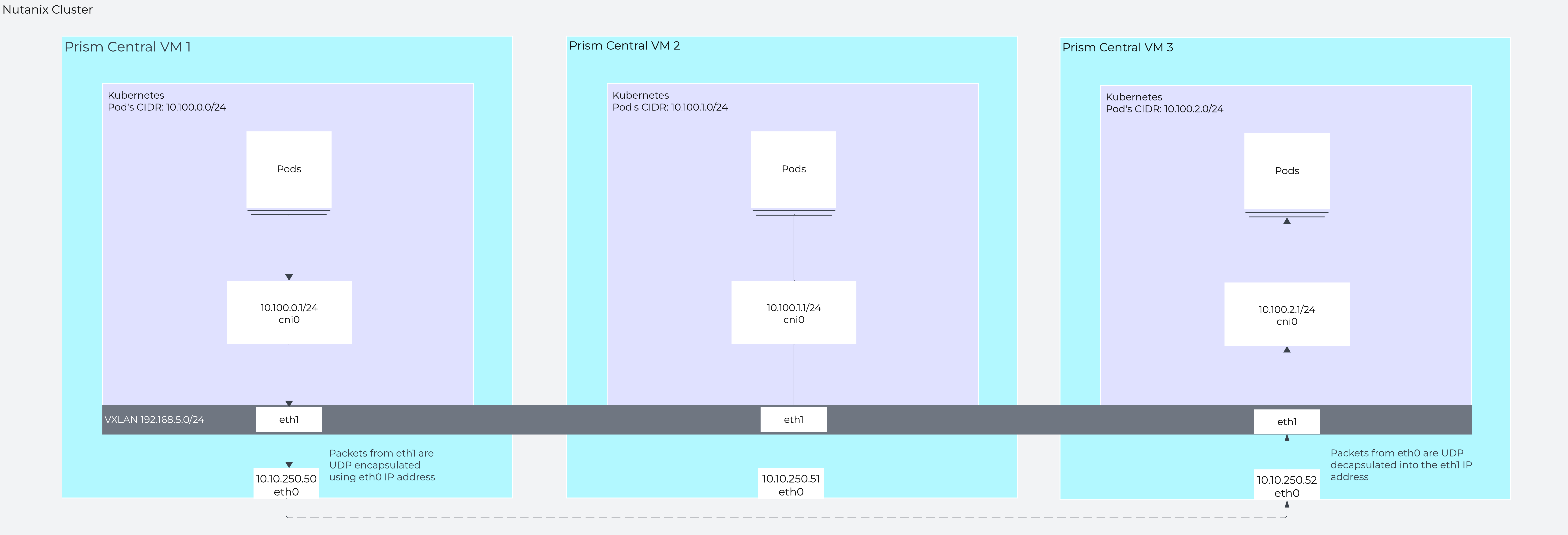 Traffic from a pod on PC VM 1 to a pod on PC VM 3
Traffic from a pod on PC VM 1 to a pod on PC VM 3
©2025 Nutanix, Inc. All rights reserved. Nutanix, the Nutanix logo and all Nutanix product and service names mentioned are registered trademarks or trademarks of Nutanix, Inc. in the United States and other countries. All other brand names mentioned are for identification purposes only and may be the trademarks of their respective holder(s).